Purpose
Terse notes on RNN’s.
- Applications
- RNN Model
- Illustration : Character-Level Language Model
- Long Short-Term Memory
- Python Code Vanilla Example
- Further Reading
Applications
RNN’s are especially adept at sequence data. They hold context in weights and can reference all elements of a sequence for ingestion and memory.
The Mathematics of a Vanilla Recurrent Neural Network
- Vanilla Forward Pass
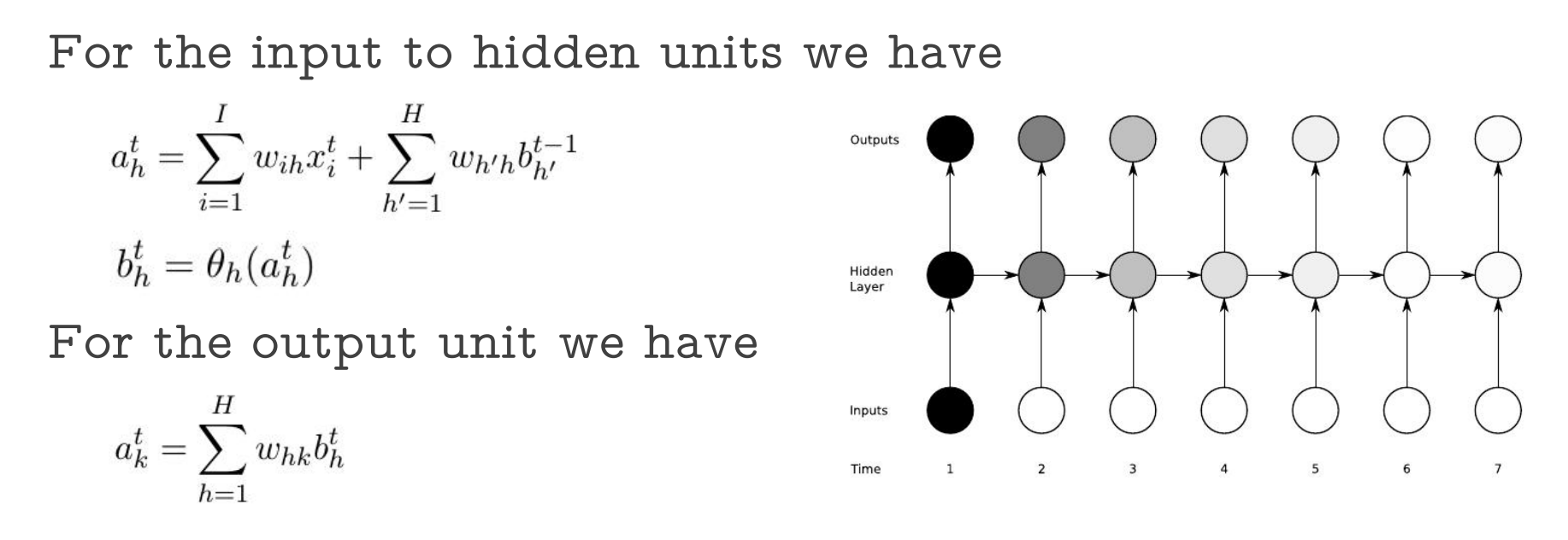
- Vanilla Backward Pass

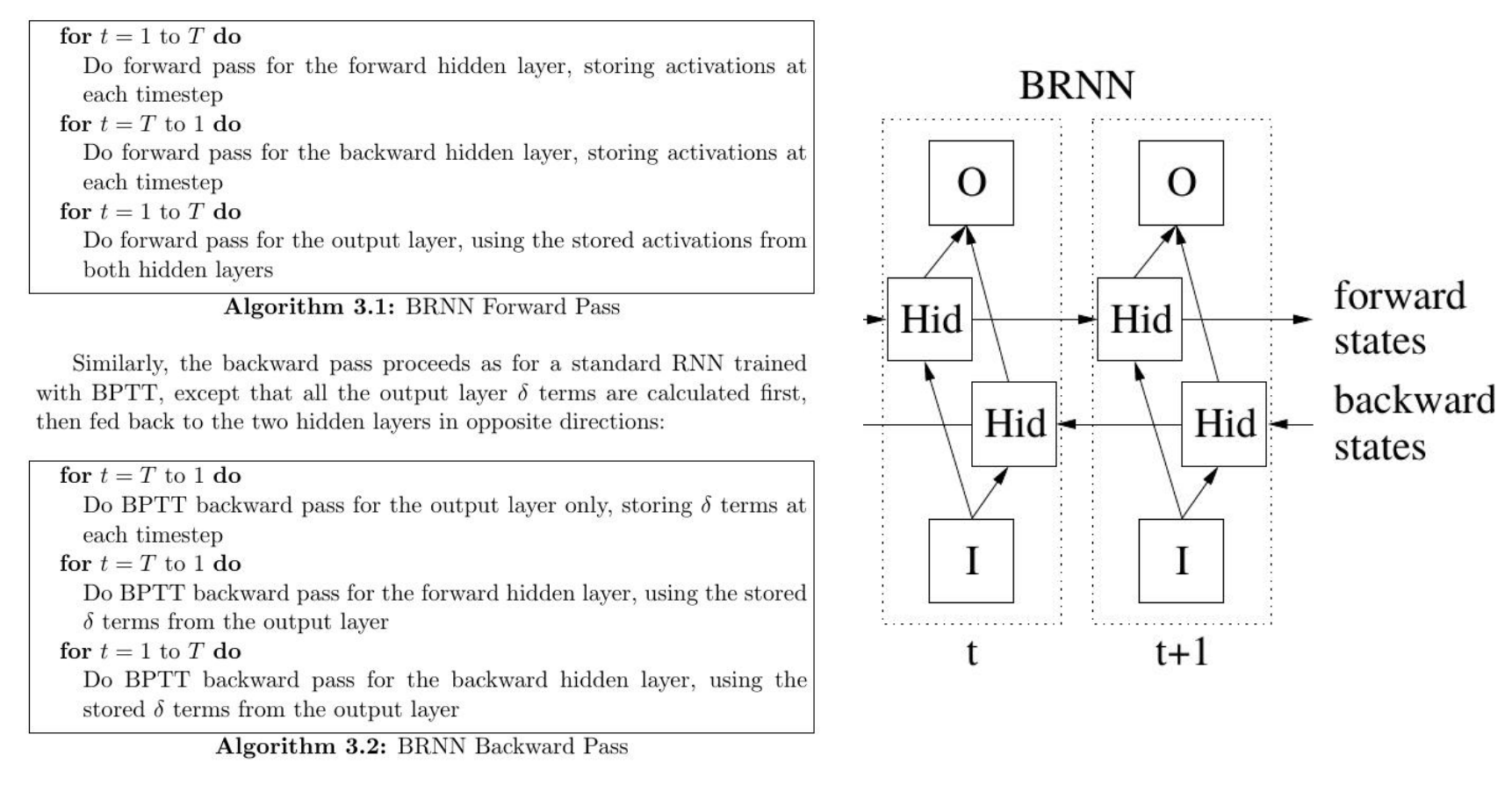
- Vanilla Bidirectional Pass
-
Training of Vanilla RNN
- Vanishing and exploding gradient problem
While training using BPTT the gradients have to travel from the last cell all the way to the first cell. The product of these gradients can go to zero or increase exponentially. The exploding gradients problem refers to the large increase in the norm of the gradient during training. The vanishing gradients problem refers to the opposite behavior, when long term components go exponentially fast to norm 0, making it impossible for the model to learn correlation between temporally distant events.
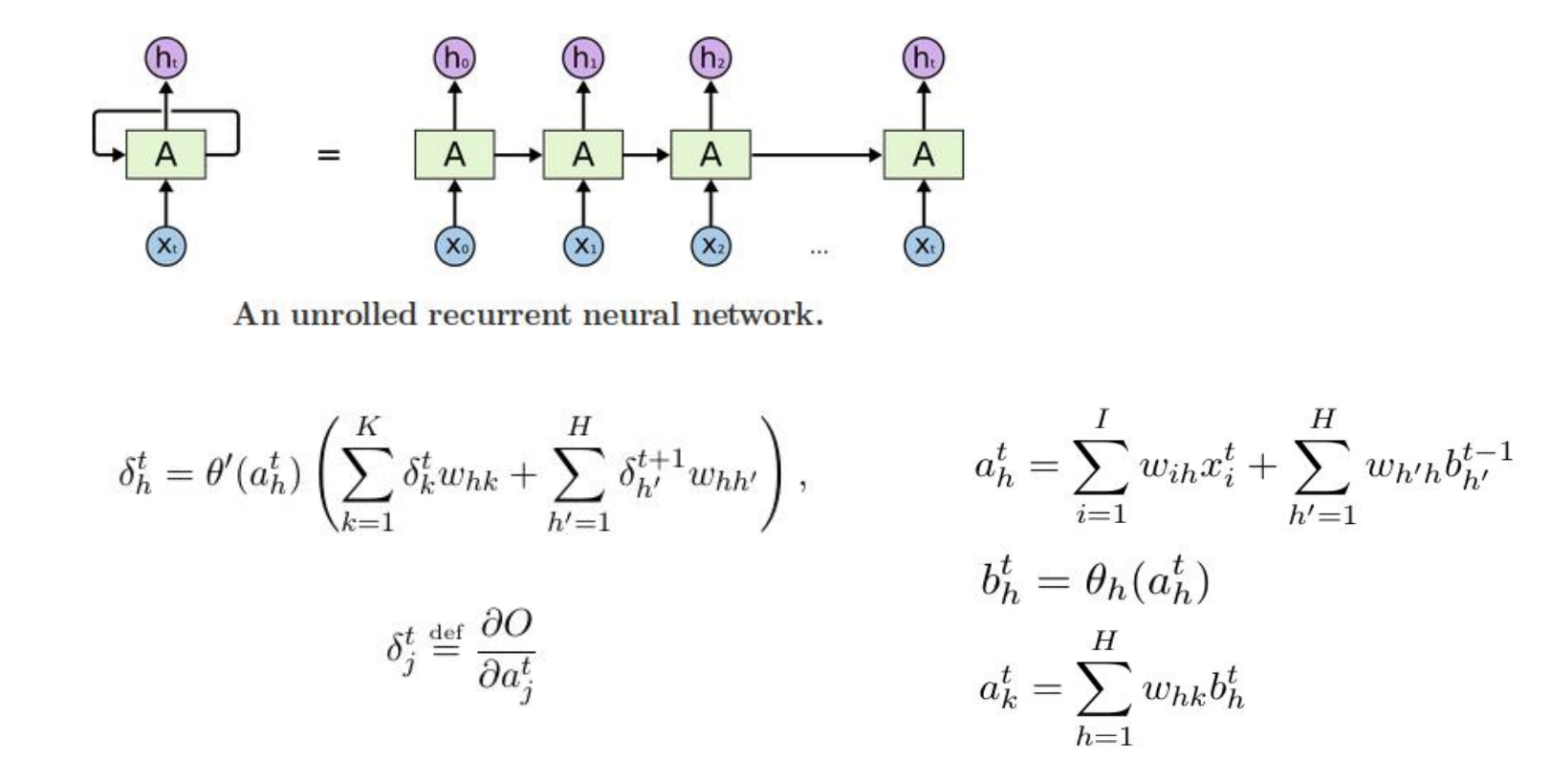
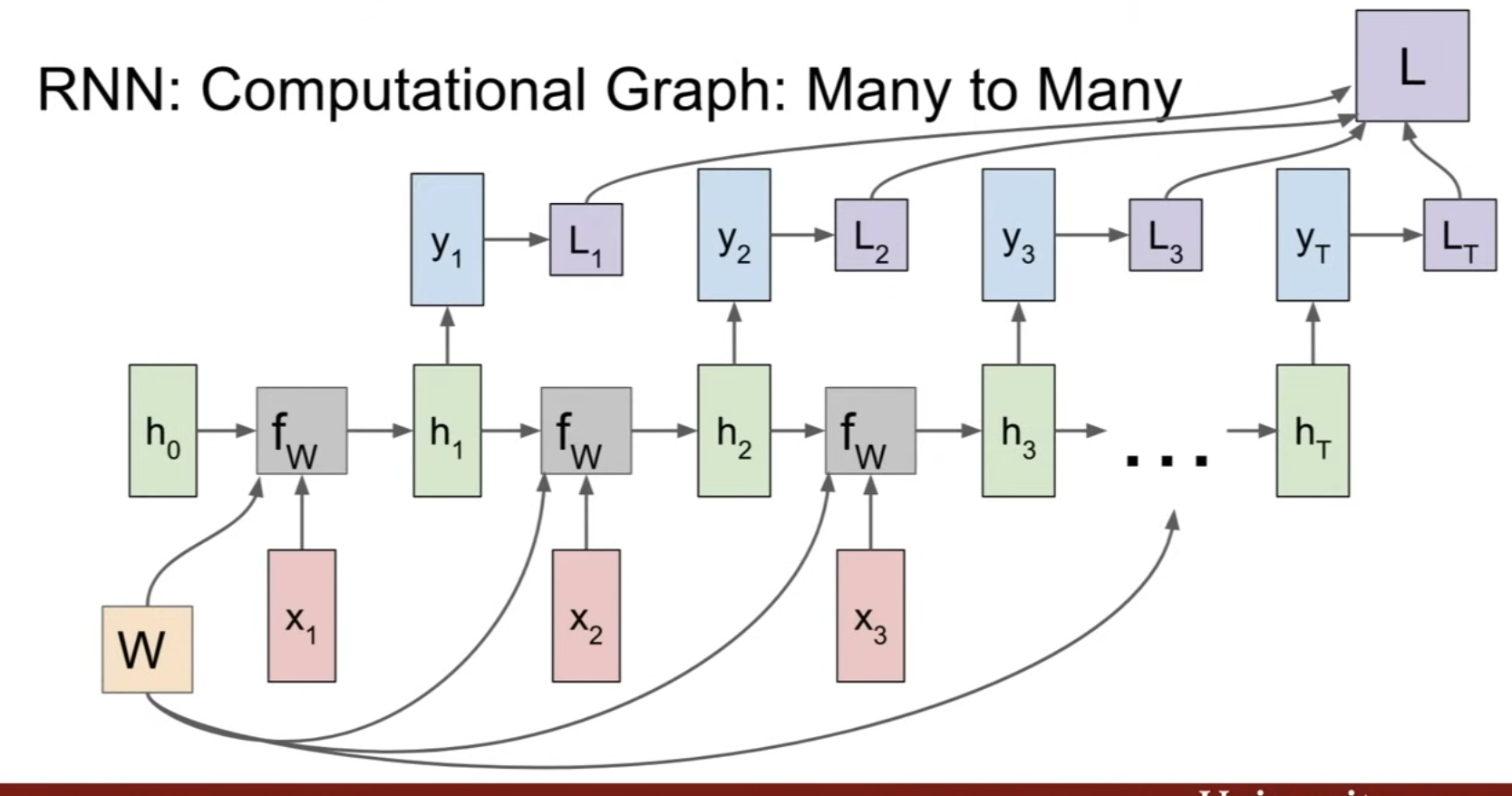
Illustration : Character-Level Language Model
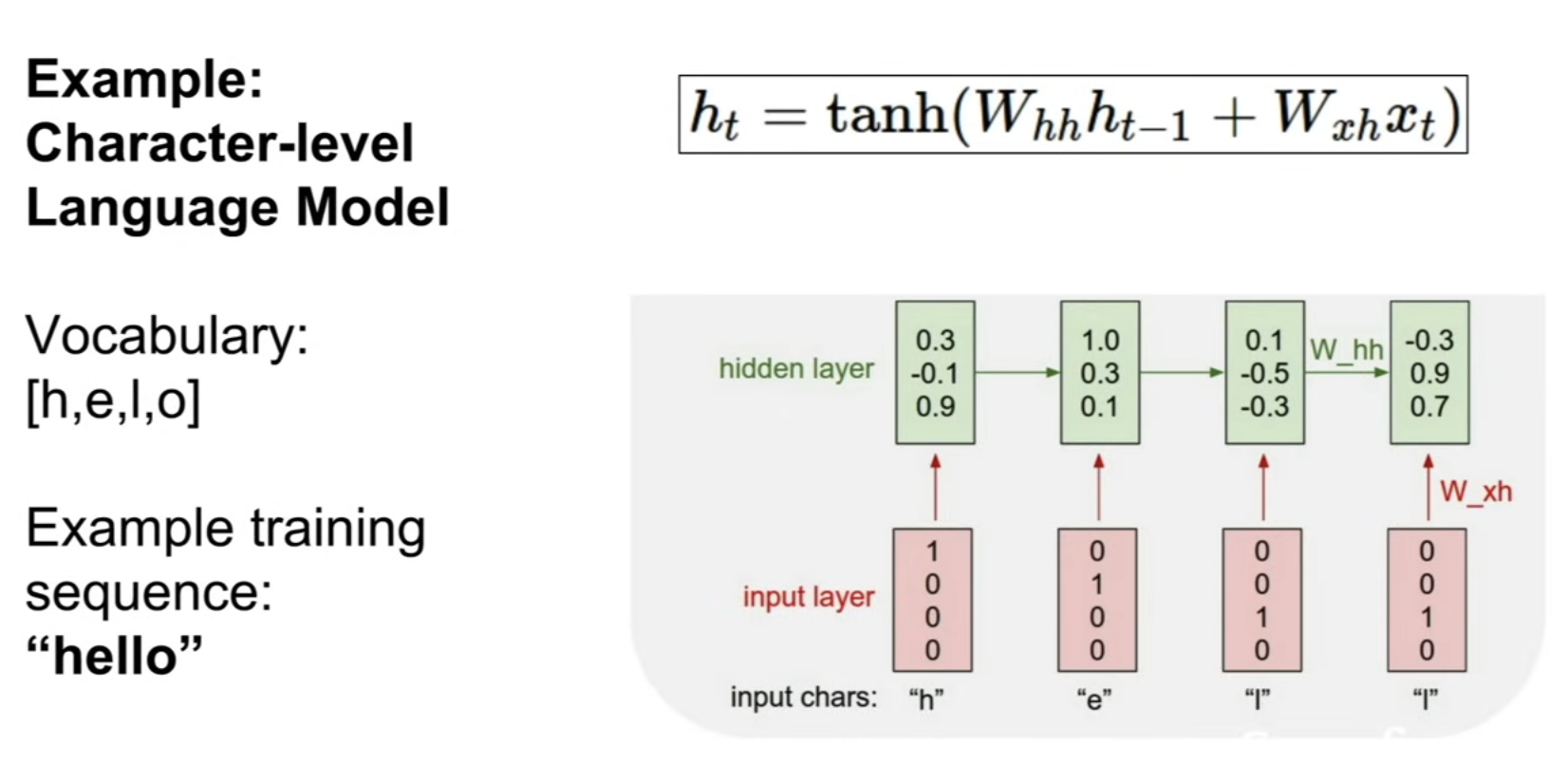
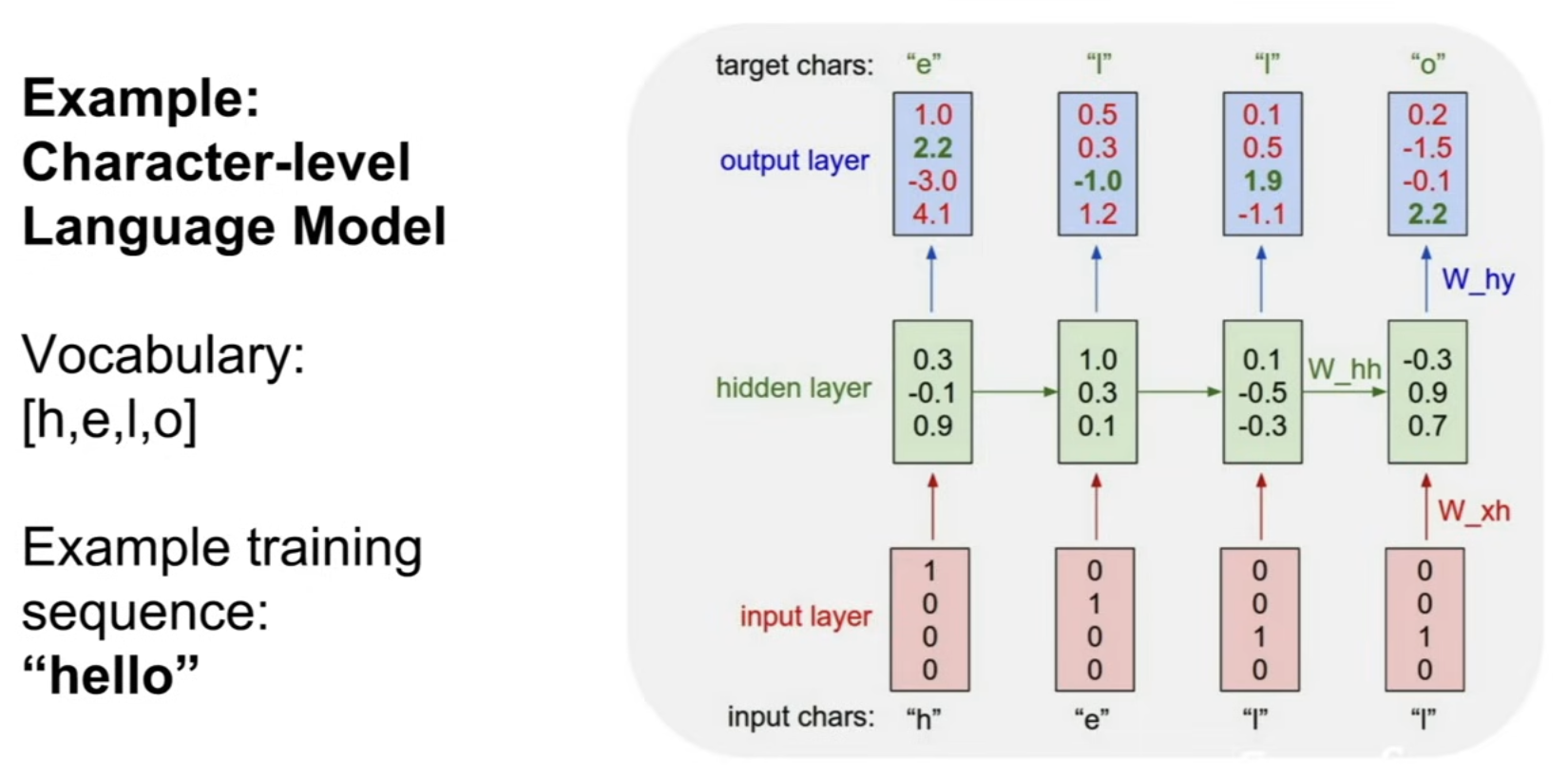
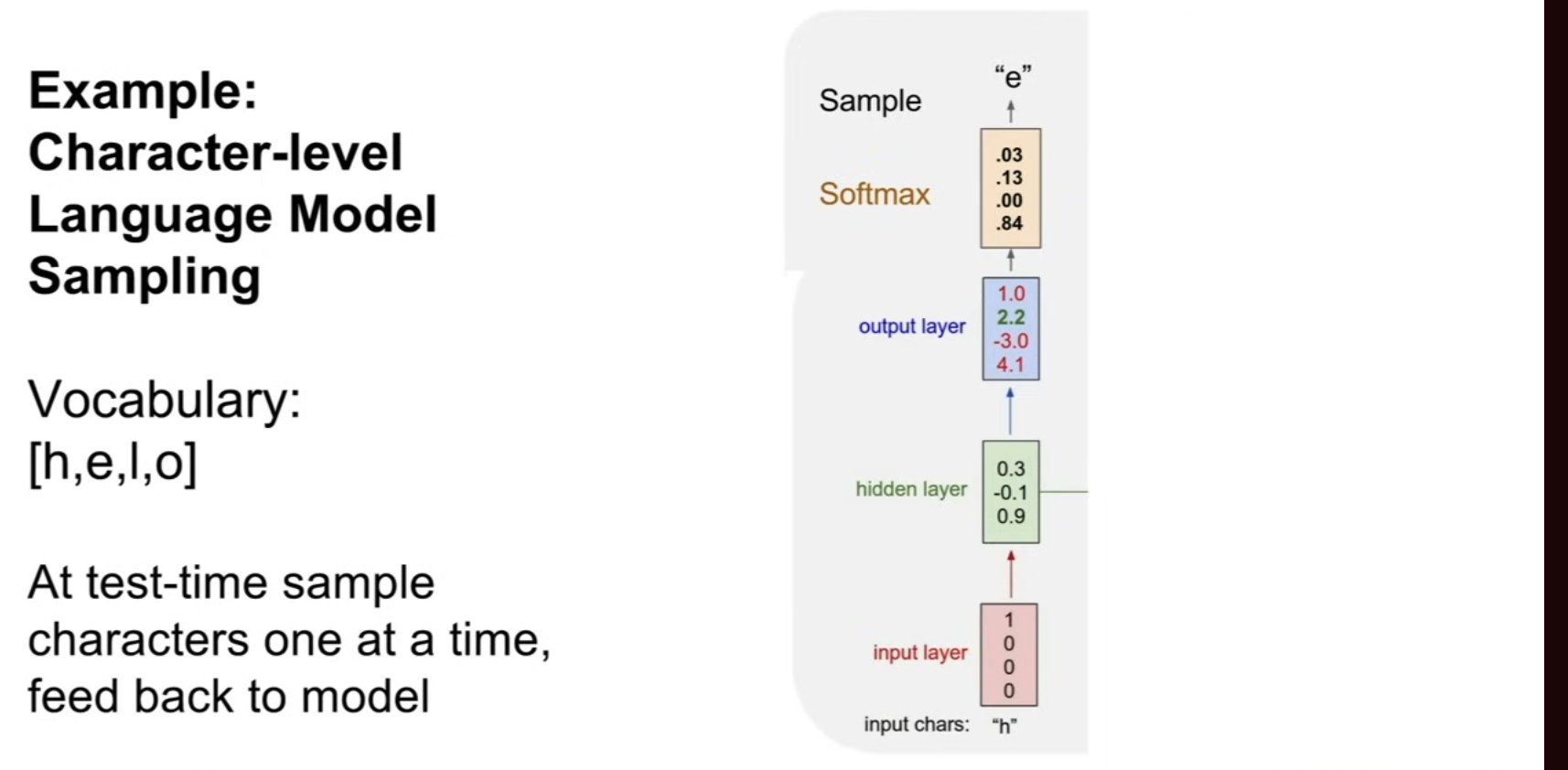
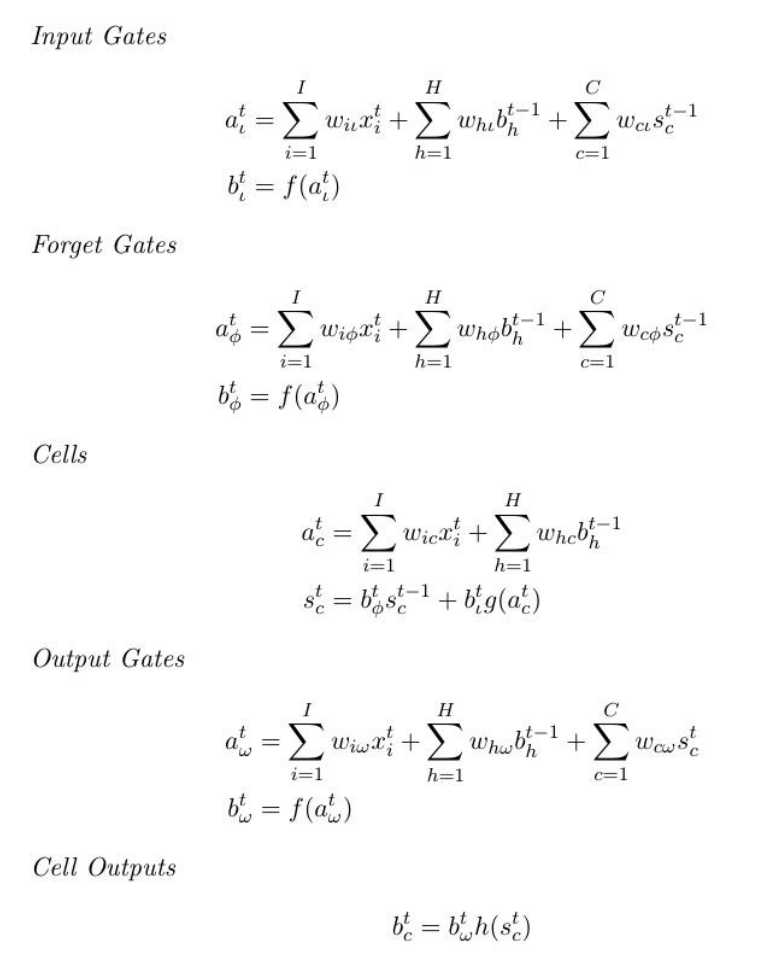
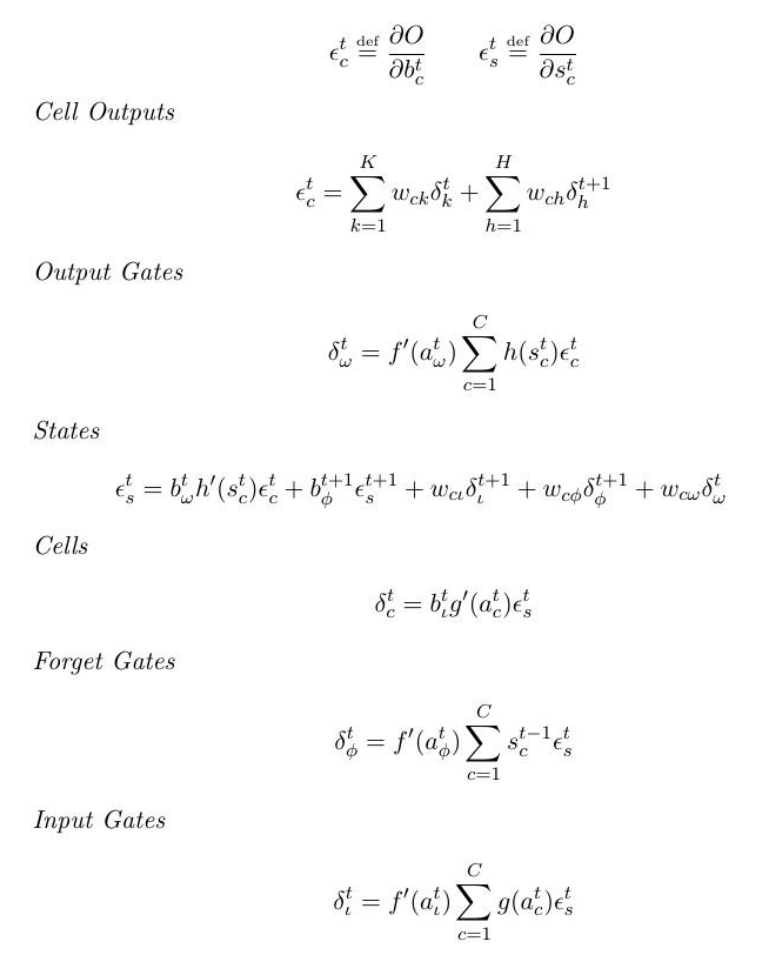
LSTM
The LSTM architecture consists of a set of recurrentlyconnectedsubnets, known as memory blocks. These blocks canbe thoughtofas a differentiable version of the memory chips in a digital computer. Each block contains one or more self-connectedmemorycells and three multiplicative units that provide continuousanalogues of write, read and reset operations for the cells: namely, the input, output and forget gates.
formulae
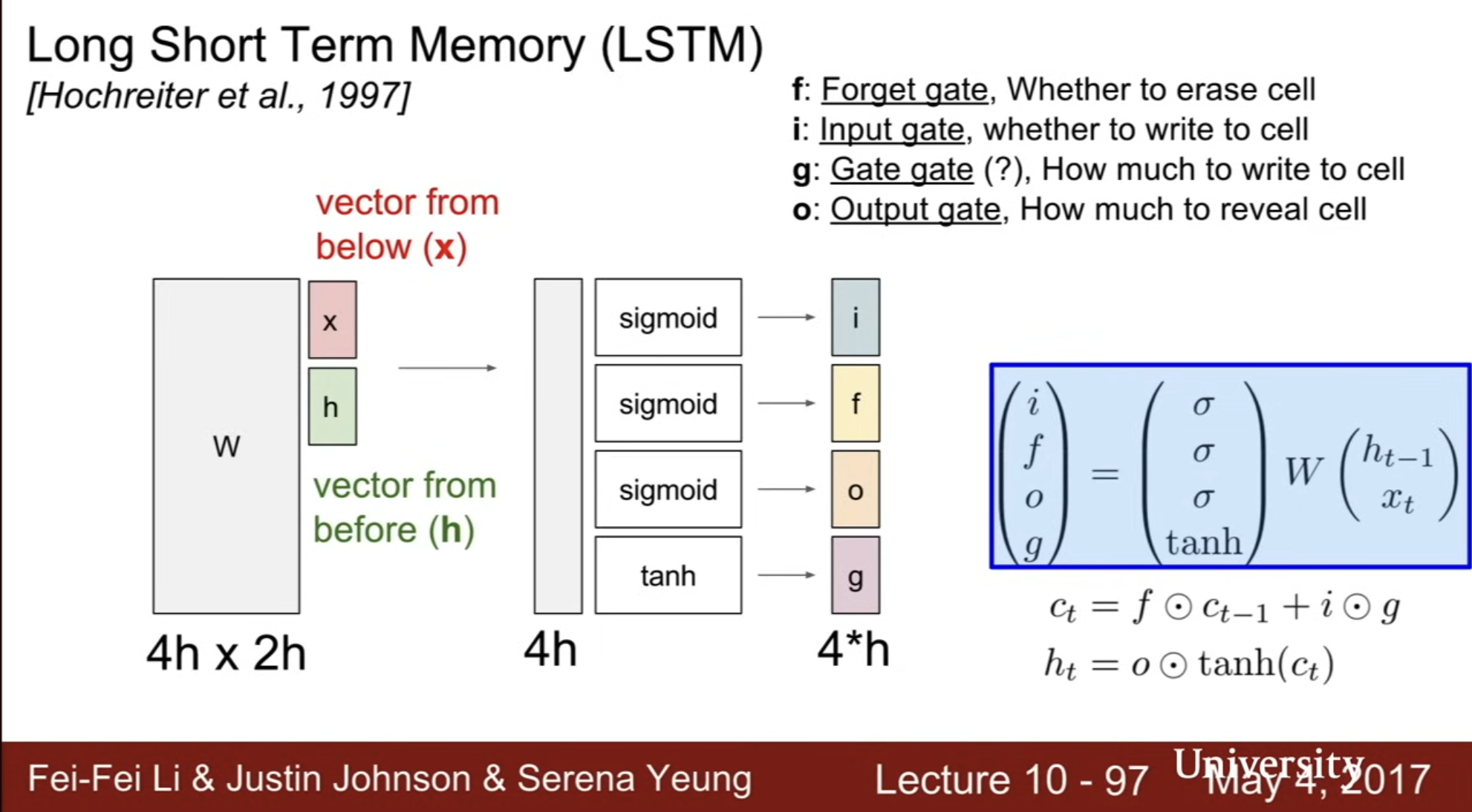
Feed-Forward LSTM equations
Feed-Backward LSTM equations
Python Code Vanilla Example (Karpathy)
Note, lines 48-58 are where backpropagation occurs and where the vanishing/exponential gradient issue arises in plain RNN.
Gist
https://gist.github.com/karpathy/d4dee566867f8291f086
Commentary Blog
https://towardsdatascience.com/recurrent-neural-networks-rnns-3f06d7653a85